Click on Picture for Enlarged View

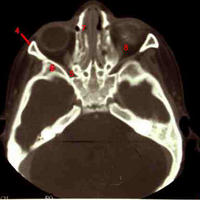
CT scan below the orbits includes a section through the auditory canal and nose to show:
1. Maxillary sinus with the nasolacrimal duct just medial.
2. Temporalis fossa with the zygomatic arch at the arrow. Note the absence of bone on the opposite site.
3. Nasal septum.
Click on picture for enlarged view.
CT scan above the opening for the nasolacrimal duct in the lacrimal fossa and includes the inferior orbital fissure.
4. zygoma
5. inferior orbital fissure (note that the fissure is oriented medially and narrows slightly posteriorly).
6. greater wing of the sphenoid
7. nasolacrimal duct
8. inferior rectus muscle
click on picture for enlarged view.

Number 7 here demonstrates the superior orbital fissure. This is most commonly mistaken for the optic canal. However, note that this opening is oriented laterally from the midline plane not medially. This is a key clue to the correct identification. Compare to the image of the CT scan that captures the optic canal below.
Click to enlarge photo

Here we see the optic canal (12 in the figure), which is of course medial to the tip of the superior orbital fissure and which is captured in this scan more laterally.
Click to enlarge the photo.
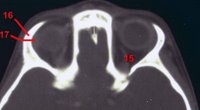
This CT image shows a level at the top of the orbit so that the lacrimal gland is evident (17). The real challenge here is number 15. This requires a great deal of knowledge. The structure starts lateral in the posterior orbit and moves medially. The immediate guess is that 15 is the superior oblique muscle. However, the origin for the superior oblique is medial to the optic canal, not lateral (
see extraocular muscle origins). Therefore this is a critical but forgotten structure, the superior ophthalmic vein, which is descending to exit the superior orbital fissure in a lower plane (
see venous drainage of the orbit). Correct identification of the dilated superior ophthalmic vein is key for the diagnosis of carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas.
Included is an excellent view of a dissected orbit.
Click here to open the image in a new window.
<
NEXT TOPIC IN OCULAR ANATOMY>
